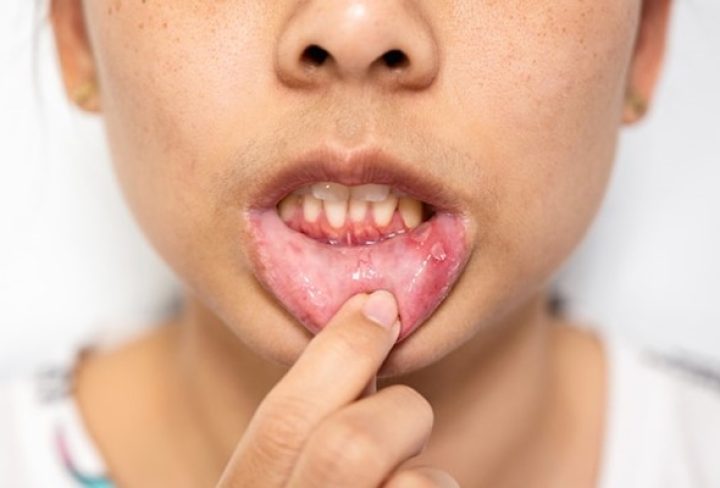
A highly contagious viral infection that causes blisters and sores.
The infection can affect people of all ages, but it is common in children under age 5.
Symptoms of Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease
- Fever
- Sore throat
- Painful sores in the mouth, on the tongue, gums, and inside cheeks
- Rash on the hands and feet, and sometimes on the buttocks and genitals
- Loss of appetite
- Irritability
Causes of Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease
- It is caused by a viral infection, most commonly Enterovirus 71 and Coxsackievirus A16.
- The virus spreads through close contact with an infected person’s saliva, mucus, or feces, or through contact with contaminated surfaces.
Diagnosis of Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease
- A doctor can usually diagnose HFMD by performing a physical examination and asking about the symptoms.
- In some cases, laboratory tests (throat swab or stool sample) may be done to confirm the diagnosis.
Treatment of Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease
There is no specific treatment for HFMD.
- Over-the-counter pain relievers to relieve pain and reduce fever.
- Drinking plenty of fluids is important to prevent dehydration.
- Eating soft, cool, and bland foods can help ease the pain of mouth sores.
- Antiviral medications may be used in severe cases.
Tips to Prevent Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease
- Frequent handwashing with soap and water, especially after using the toilet, changing diapers, and before preparing food.
- Avoid close contact with people who have HFMD.
- Disinfect frequently touched surfaces, such as toys and doorknobs.
- Keep sick children home from school or day-care until they are no longer contagious.
Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease: When to See a Doctor?
- Your child’s symptoms do not improve after 7 to 10 days
- Your child has a very high temperature or feels hot and shivery
- Your child is dehydrated (they’re not peeing as often as usual)
Fast facts on Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease
- HFMD is a common illness in children, especially those under the age of 5.
- The virus that causes HFMD is highly contagious and can spread quickly in day-care centers and schools.
- Most people recover from HFMD without complications within 7-10 days.
- In rare cases, complications such as viral meningitis or encephalitis can occur.
- There is no vaccine available to prevent HFMD.
Myth and Fact: Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease
Myth: Hand, foot, and mouth disease is caused by poor hygiene.
Fact: Hand, foot, and mouth disease is caused by a viral infection, and good hygiene practices can help prevent the spread of the illness but are not the cause of it.
FAQ’S: Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease
Q: Is there a vaccine for hand, foot, and mouth disease? A: Currently, no vaccine is available to prevent hand, foot, and mouth disease.
Q: How long is someone contagious with hand, foot, and mouth disease?
A: Someone with hand, foot, and mouth disease is contagious until their symptoms have resolved, usually taking 7-10 days.
FAQ’S: Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease
How Reduce the Spread of Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease?
- Wash your hands frequently with soap and water, and make sure children wash their hands too.
- Use tissues when coughing or sneezing to prevent the spread of germs. Dispose of used tissues promptly.
- Avoid sharing household items such as towels, cups, and cutlery.
- Wash any soiled bedding or clothing on a hot wash to kill germs.